Note
Click here to download the full example code
Customizing head shape with Homer Simpson
For additional context, check out FixingHomer.com. TLDR: We take this fun image and show how flexible the NDK is for transcranial ultrasound simulation.
The following step downloads and loads numpy material masks The masks were generated using in the image from fixinghomer.com
import numpy as np
import pooch
import neurotechdevkit as ndk
masks_url = "https://neurotechdevkit.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/homer_masks.npz"
known_hash = "9f58e7d1f68f45466ee5fe848a83dd8eb676139672c44af5214231b3e3fe6fb9"
downloaded_file_path = pooch.retrieve(
masks_url, known_hash=known_hash, progressbar=True
)
with np.load(downloaded_file_path) as data:
masks = dict(data)
masks = {k: v.astype(np.bool_) for k, v in masks.items()}
Out:
0%| | 0.00/2.17M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
2%|▉ | 54.3k/2.17M [00:00<00:04, 432kB/s]
14%|█████▎ | 303k/2.17M [00:00<00:01, 1.33MB/s]
39%|██████████████▊ | 846k/2.17M [00:00<00:00, 2.68MB/s]
0%| | 0.00/2.17M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
100%|█████████████████████████████████████| 2.17M/2.17M [00:00<00:00, 4.88GB/s]
Setup the scenario using the NDK
extent = (
0.1355,
0.1205,
) # (x, y) in meters.
# This size matches the size of the image from fixinghomer.com at 272x242,
# given our other chosen parameters (`ppw` and `center_frequency`)
target_center = [0.036, 0.067] # target positioned on his brain
target_radius = 0.004
center_frequency = 5e5
# define the brainstem material (the other materials used here are standard in the NDK)
brainstem_mat = ndk.materials.Material(
vp=1540.0, rho=1000.0, alpha=0.001, render_color="#510400"
)
# adjust cortical bone properties to handle the unusual head shape and skull thickness
cortical_bone_mat = ndk.materials.Material(
vp=1800, rho=3350, alpha=2.37, render_color="#FAF0CA"
)
# Define the Scenario in 2 dimensions
scenario = ndk.scenarios.Scenario2D(
material_properties={
"brainstem": brainstem_mat,
"cortical_bone": cortical_bone_mat,
# the other materials are standard in the NDK
}
)
# specify the target marker
scenario.target = ndk.scenarios.Target(
target_id="target_1",
center=target_center,
radius=target_radius,
description="cortex, posterior",
)
Next, we add the source transducer.
source_position = [0.02, 0.1]
source_target = [0.037, 0.067]
source = ndk.sources.FocusedSource2D(
position=source_position,
direction=np.array(source_target) - np.array(source_position),
aperture=0.05,
focal_length=0.038,
num_points=1000,
)
# The failed scenario shown on fixinghomer.com is commented here for reference.
# failed_source_position=[0.08, 0.106]
# failed_source_target = [0.037, 0.067]
# failed_source = ndk.sources.FocusedSource2D(
# position=failed_source_position,
# direction=np.array(failed_source_target) - np.array(failed_source_position),
# aperture=0.04, # width of the source
# focal_length=0.06, #distance to focal point
# num_points=1000,
# )
scenario.sources = [source] # , failed_source]
scenario.origin = [0, 0]
scenario.material_outline_upsample_factor = 8
scenario.center_frequency = center_frequency # Hz
grid = ndk.grid.Grid.make_grid(
extent=extent, # m
speed_water=1500,
center_frequency=scenario.center_frequency,
ppw=6,
)
scenario.grid = grid
# confirm that the grid size matches the image size of 272x242
print("total voxels:")
print(grid.space.shape[0], grid.space.shape[1])
dx = grid.space.spacing[0]
scenario.material_masks = masks
Out:
Now, we are ready to review the layout, and run the simulation.
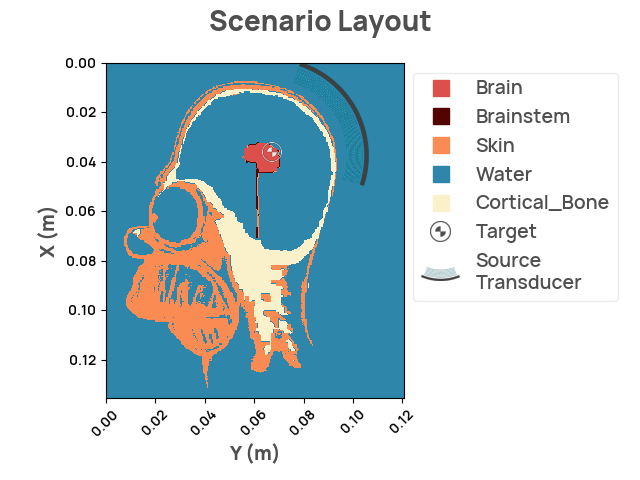
Set up the Problem
problem = ndk.problem.Problem(grid=grid)
problem.add_material_fields(
materials=scenario.materials,
masks=scenario.material_masks,
)
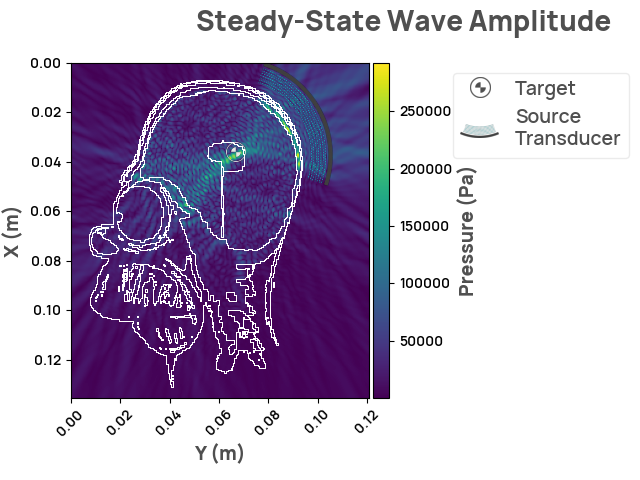
Rendering the simulation
scenario.problem = problem
result = scenario.simulate_steady_state()
assert isinstance(result, ndk.results.SteadyStateResult2D)
result.render_steady_state_amplitudes(show_material_outlines=True)
Out:
Estimated time to complete simulation: 52 seconds. Memory required is 8.128512230525773 GB (available 73.624408064 GB). These values are approximated.
/home/circleci/.cache/pypoetry/virtualenvs/neurotechdevkit-3aSsmiER-py3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/devito/finite_differences/differentiable.py:224: DeprecationWarning: NotImplemented should not be used in a boolean context
return super(Differentiable, self).__eq__(other) and\
/home/circleci/.cache/pypoetry/virtualenvs/neurotechdevkit-3aSsmiER-py3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/devito/finite_differences/differentiable.py:224: DeprecationWarning: NotImplemented should not be used in a boolean context
return super(Differentiable, self).__eq__(other) and\
gcc -O3 -g -fPIC -Wall -std=c99 -march=native -Wno-unused-result -Wno-unused-variable -Wno-unused-but-set-variable -ffast-math -shared -fopenmp /tmp/devito-jitcache-uid1001/5800f06382eac00db301260ceef0ff2ba66ea5f0.c -lm -o /tmp/devito-jitcache-uid1001/5800f06382eac00db301260ceef0ff2ba66ea5f0.so
We've successfully hit the target, and can proceed with treatment for Homer! FixingHomer.com
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 32.200 seconds)
Download Python source code: plot_homer.py